Strain
Bat_KT444582
(Region: China; Strain: SARS-like coronavirus WIV16, complete genome.; Date: 21-Jul-13)
Gene
hypothetical protein
Description
Annotated in NCBI,
hypothetical protein
Location
GenBank Accession
Full name
Spike glycoprotein
Alternative Name
E2
Peplomer protein
Peplomer protein
Sequence
CDS
ATGTTACTTTTAGTAACATTGTTTGGTTTAGCATCAGGGTGCAGCTTACCACTTACGGTTAGCTGCCCTAGAGGCCTACCTTTCACTCTACAGATTAACACTACTAGTGTTACTGTGGAGTGGTATCGGGTATCTCCTGCATCAATGCAAGGTCTTACAAAGATAAATACTGGCAGCACTATTTTTGATAACAACTTTAGTGTAGTCAATAATAATTTGTACTTCAAACAGTGTTTTGGAGGCTTTTTTTTACAGCACGCTGTTACCGCCAGGGTAAGCATGACGGTGCTATAG
Protein
MLLLVTLFGLASGCSLPLTVSCPRGLPFTLQINTTSVTVEWYRVSPASMQGLTKINTGSTIFDNNFSVVNNNLYFKQCFGGFFLQHAVTARVSMTVL
Summary
Function
Spike protein S1: attaches the virion to the cell membrane by interacting with host receptor, initiating the infection.
Spike protein S2': Acts as a viral fusion peptide which is unmasked following S2 cleavage occurring upon virus endocytosis.
Spike protein S2: mediates fusion of the virion and cellular membranes by acting as a class I viral fusion protein. Under the current model, the protein has at least three conformational states: pre-fusion native state, pre-hairpin intermediate state, and post-fusion hairpin state. During viral and target cell membrane fusion, the coiled coil regions (heptad repeats) assume a trimer-of-hairpins structure, positioning the fusion peptide in close proximity to the C-terminal region of the ectodomain. The formation of this structure appears to drive apposition and subsequent fusion of viral and target cell membranes.
Spike protein S2': Acts as a viral fusion peptide which is unmasked following S2 cleavage occurring upon virus endocytosis.
Spike protein S2: mediates fusion of the virion and cellular membranes by acting as a class I viral fusion protein. Under the current model, the protein has at least three conformational states: pre-fusion native state, pre-hairpin intermediate state, and post-fusion hairpin state. During viral and target cell membrane fusion, the coiled coil regions (heptad repeats) assume a trimer-of-hairpins structure, positioning the fusion peptide in close proximity to the C-terminal region of the ectodomain. The formation of this structure appears to drive apposition and subsequent fusion of viral and target cell membranes.
Subunit
Homotrimer; each monomer consists of a S1 and a S2 subunit. The resulting peplomers protrude from the virus surface as spikes.
Similarity
Belongs to the betacoronaviruses spike protein family.
Feature
chain Spike protein S2
Uniprot
Pubmed
EMBL
Interpro
SUPFAM
SSF143587
SSF143587
Gene 3D
ProteinModelPortal
Ontologies
GO
GO:0019064 P:fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane
GO:0009405 P:pathogenesis
GO:0039654 P:fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane
GO:0046813 P:receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell
GO:0020002 C:host cell plasma membrane
GO:0055036 C:virion membrane
GO:0075509 P:endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell
GO:0016021 C:integral component of membrane
GO:0019031 C:viral envelope
GO:0044173 C:host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane
GO:0009405 P:pathogenesis
GO:0039654 P:fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane
GO:0046813 P:receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell
GO:0020002 C:host cell plasma membrane
GO:0055036 C:virion membrane
GO:0075509 P:endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell
GO:0016021 C:integral component of membrane
GO:0019031 C:viral envelope
GO:0044173 C:host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane
Subcellular Location
From MSLVP
Multi-Pass Membrane
From Uniprot
Virion membrane
Accumulates in the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment, where it participates in virus particle assembly. Some S oligomers are transported to the host plasma membrane, where they may mediate cell-cell fusion. With evidence from 1 publications.
Host endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane Accumulates in the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment, where it participates in virus particle assembly. Some S oligomers are transported to the host plasma membrane, where they may mediate cell-cell fusion. With evidence from 1 publications.
Host cell membrane Accumulates in the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment, where it participates in virus particle assembly. Some S oligomers are transported to the host plasma membrane, where they may mediate cell-cell fusion. With evidence from 1 publications.
Host endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane Accumulates in the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment, where it participates in virus particle assembly. Some S oligomers are transported to the host plasma membrane, where they may mediate cell-cell fusion. With evidence from 1 publications.
Host cell membrane Accumulates in the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment, where it participates in virus particle assembly. Some S oligomers are transported to the host plasma membrane, where they may mediate cell-cell fusion. With evidence from 1 publications.
Topology
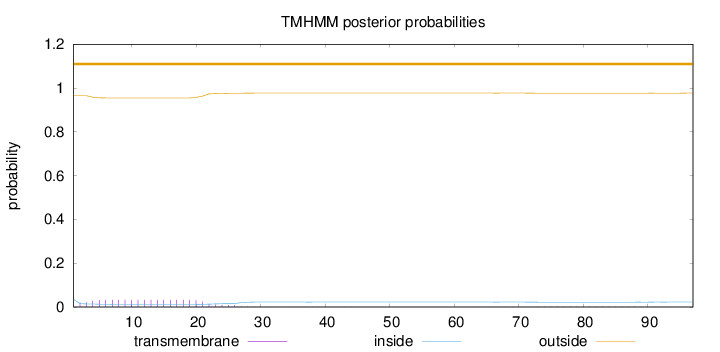
Length:
97
Number of predicted TMHs:
0
Exp number of AAs in TMHs:
0.72381
Exp number, first 60 AAs:
0.67927
Total prob of N-in:
0.03494
outside
1 - 97